Guides
Install GIS Cloud Suite in the user interface
Used to quickly deploy GIS cloud suite in Kubernetes environment through the installation wizard provided by SuperMap iManager Deployment Center.
Installation
Notes:
- If you have previously installed the GIS Cloud Suite through the Deployment Center and need a new environment, please first uninstallin the Deployment Center->Deployment interface, and then reinstall. For GIS Cloud Suite environments deployed by other methods, you need to uninstall using the corresponding method.
When you install again, your last configuration options will be retained so that you can quickly complete the corresponding configuration.
- If the license center has been deployed in your environment, the account password must be the same as the last time, so please set it carefully! If the business needs to modify the license center account password for the second time, please uninstall the deployed GIS cloud suite first, clear the /opt/bslicense/data directory on the kubernetes node, redeploy the GIS cloud suite, complete the setting of the license center account password during the deployment process, and go to the license center to re-import the license file after the deployment is complete.
- Start SuperMap iManager Deployment Center and access it, enter the Deployment interface, and click Getting Started.
- Select Product, select SuperMap GIS Cloud Suite, and click the Next button.
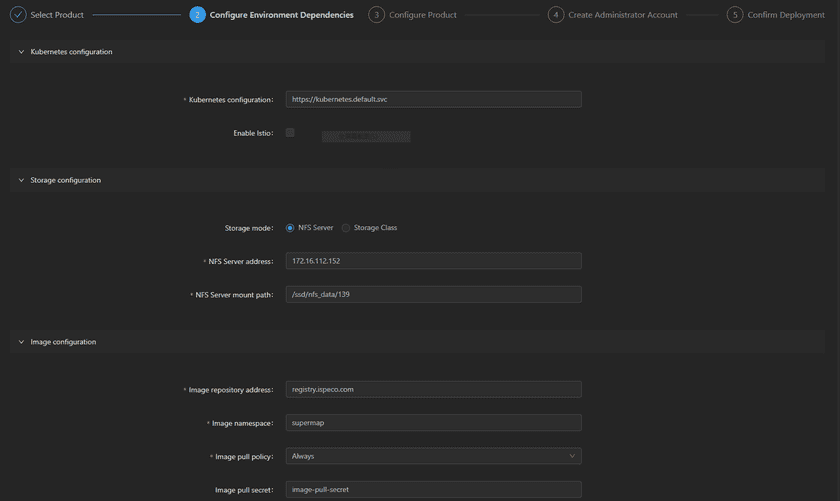
- Configure Environment Dependencies. Basic configuration items include Kubernetes configuration, storage configuration, and image configuration. You can fill in or modify the default values as needed. In the advanced options, you can configure Kubernetes node affinity and tolerance to control how Pods are scheduled in the cluster to meet your resource requirements and operating constraints. After the configuration is completed, click the Next button.
3.1 Basic configuration
-
Kubernetes configuration:You can configure the URL address of the K8s Master node and Enable/Disable the service mesh.
Kubernetes Server address defaults to
https://kubernetes.default.svc. Usually, you can keep the default value. If the K8s environment is provided by a public cloud such as Alibaba Cloud, you need to fill in the URL of the actual K8s master node. You can use the command “kubectl cluster-info” to view the K8s cluster information. For example,https://192.168.17.110:6443。 -
Storage configuration: Provides two methods: NFS Server and StorageClass to store iManager data.
- NFS Server:You need to install NFS Client in the Node machine of K8s. NFS Server address Fill in your NFS Server address, which can be either IP or domain name. NFS Server mount path is the root path (/) by default . Please fill in the path according to your NFS installation. If you use the NFS offline installation package provided by SuperMap Install NFS, the address here is: /opt/nfs_data.
- StorageClass:Supports filling in the StorageClass name corresponding to Ceph storage or Longhorn storage.
-
Image configuration: You can fill in the configuration related to the iManager image repository to pull the image required for deploying iManager.
Image repository address is the Alibaba Cloud warehouse
registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.comby defaults, which is recommended when using the Internet; if you use the intranet, the warehouse is configured as<ip>:5000,<ip>is the IP address of the machine where the image repository is located.Image namespace defaults to supermap, but can also be customized.
Image pull policy provides three modes: IfNotPresent, Always, Never, which respectively mean “if there is an available image locally, use the local image, otherwise pull it from the image repository”, “always pull the latest image from the image repository”, and “do not pull the image from the image repository”. IfNotPresent is selected by default. Imange pull secret is used for identity authentication when pulling private images. You can fill in image-pull-secret. If you configure a private repository, please refer to FAQ(Tutorial -> Appendix -> FAQ -> Question 6)。
3.2 Advanced Options
-
Node affinity configuration: You can configure node scheduling modes separately under Required scheduling and Preferred scheduling.
Requered ensures that Pods must be scheduled on nodes that satisfy the node affinity rules. In label settings, you can set label keys, operators, and label values. Operators can be selected as “In” (the value of the matching label key must be one of the provided list), “NotIn” (the value of the matching label key cannot be any of the provided list), “Exists” (the matching label key must exist regardless of its value), “DoesNotExist” (the matching label key must not exist), “Gt” (the value of the matching label key must be greater than the provided value), or “Lt” (the value of the matching label key must be less than the provided value). In addition, you can add new labels.
Preferred allows Pods to be scheduled while meeting node affinity rules as much as possible, but not necessarily. You can set label keys, operators, label values, and weights. You can configure multiple label values separated by ”;“. In addition, you can add new labels and add multiple sets of preference settings.
-
Node roleration configuration: By setting the node’s toleration, Pods can be scheduled on nodes with specific taints.
You can set the label key, operator, label value, and policy. For the operator, you can choose “Equal” or “Exists”, and for the policy, you can choose “NoSchedule”, “PreferNoSchedule”, or “NoExecute”. In addition, you can add new labels.
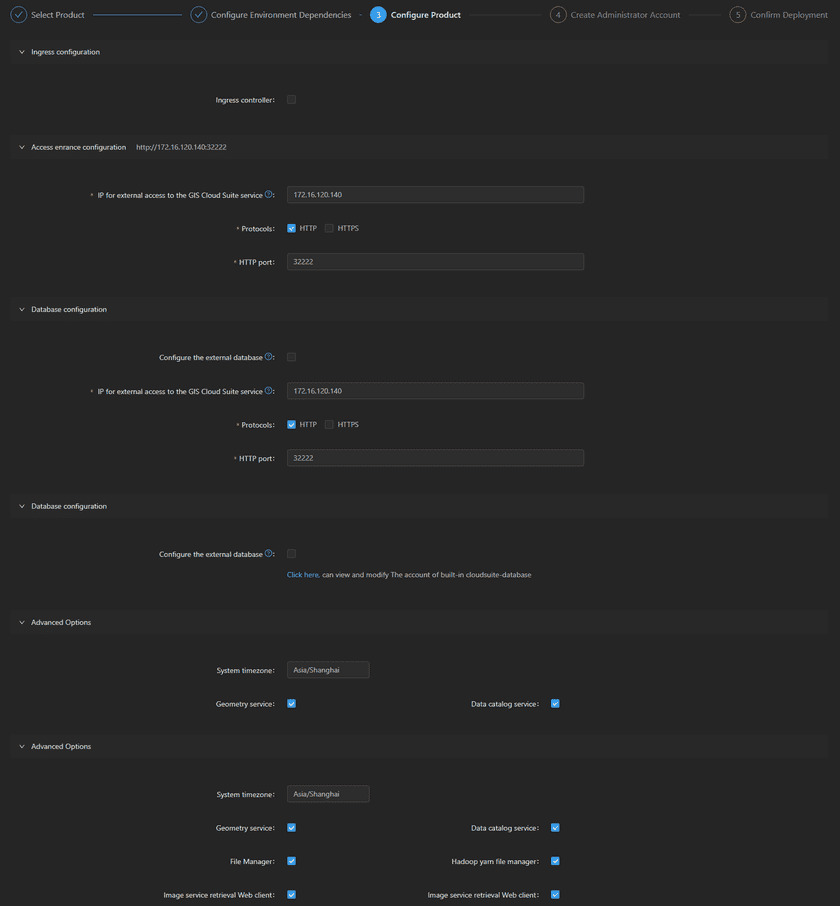
- Configure Product,The basic configuration items include Ingress configuration, access entry configuration, and database configuration. You can fill in or modify the default values as needed according to the actual situation. In the advanced options, you can choose to enable/disable a variety of built-in service capabilities according to your needs, including: geometry service, file manager, system monitoring service, log harvesting service, iPortal-related services, etc., and support the configuration of external licensing center, RabbitMQ, Keycloak and other services. After the configuration is completed, click the Next button.
4.1 Basic configuration
- Ingress configuration: After using the Ingress controller, you can set the domain name. It will provide two service types: ClusterIP and LoadBalancer. ClusterIP is selected by default. If the K8s environment is provided by a public cloud such as Alibaba Cloud, select LoadBalancer. Domain mapped Kubernetes node IP is required if you choose the ClusterIP type or need to configure the access entry domain name. It is optional when you choose the LoadBalancer type. The first K8s node IP is used by default.
- Access entrance configuration:You can use the domain name only after enabling the Ingress controller. You can modify the IP address for external access to the GIS Cloud Suite service. It is recommended to fill in the K8s Master node IP (or proxy IP)/cloud vendor elastic public network IP address. You can also specify the HTTP or HTTPS access protocol and configure its external port. For details, please refer to GIS Cloud Suite Management(Tutorial -> Site Management -> GIS Cloud Suite -> GIS Cloud Suite Management -> “Configuration”)。
- Database configuration: You can enable Configure the external database. If not enabled, the PostgreSQL database provided by the system will be used by default.
4.2 Advanced Options
- System timezone: The relative path of the time zone file in the system time zone directory (/usr/share/zoneinfo/). Usually the default value is Asia/Shanghai. You can modify it as needed, for example: America/New_York
- Geometry service: Whether to enable the built-in Geometry service
- Data catalog service: Whether to enable the built-in Data catalog service:
- File Manager: Whether to enable the built-in File Manager
- hadoop yarn file manager: Whether to enable the built-in Hadoop YARN file manager
- Stream processing model: Whether to enable the built-in Stream processing model
- Image service retrieval Web client: Whether to enable the built-in Image service retrieval Web client
- Geoprocessing file manager: Whether to enable the built-in Geoprocessing service file manager
- Built in service for copying and mounting Oracle clients: Whether to enable this service. If you want to publish an Oracle workspacedata source, please enable this service for use by the GIS service instance
- Command line and view container log service: Whether to enable the built-in container management function
You can choose whether to enable System monitoring service (Prometheus), Log harvesting service and iPortal service as needed, and provide multiple sub-function services. You can select and configure external services as needed. Before enabling iPortal service, you need to ensure that the system has sufficient resources.
If the license center, message notification, gateway Redis, user center Keycloak and its database need to be configured as external services, you can enable Configure external Bslicense service, Configure the external RabbitMQ service (RabbitMQ), Configure the external Redis service, Configure the external Keycloak service and Configure the external Keycloak database as needed. When configuring, please fill in the accurate host name, port, account password and other information of the external service.
- Create Administrator Account, After filling in the administrator username and password, click the Next button.
- Confirm Deployment, Before the system is officially deployed, you can return to the previous steps to confirm or modify the information again, and then click the one-click deployment button after confirmation.
During the system deployment process, you can use the progress bar to understand the real-time deployment status. The final deployment result may include some service startup failures and deployment failures:
- Deployment is successful but some services fail to start: The “Deployment” interface will remind you to pay attention in time. You can find the corresponding service under the “Basic Services” list in the iManager interface and try to redeploy.
- Deployment failure: You can choose Uninstall and reinstall or go to the previous configuration step Return to modify, reconfigure and try to deploy again.
View deployment information
After the GIS Cloud Suite is installed, you can view the product name, product introduction, product version, deployment time, and access address in the Deployment Center->Deployment interface. Click “Access Address” to jump to the login interface. You can also uninstall the GIS Cloud Suite currently installed through the Deployment Center with one click.
Enter the Deployment Center->About interface, and you can also learn about the version and other information of the GIS Cloud Suite that has been deployed.
Notes:
- If you forget the administrator password, you can reset it.
- After the GIS Cloud Suite is deployed, it is recommended that you disable the deployment center. For the deactivation/enabling method, see Deployment Center->Disable/Enable Deployment Center.
Configure licensing
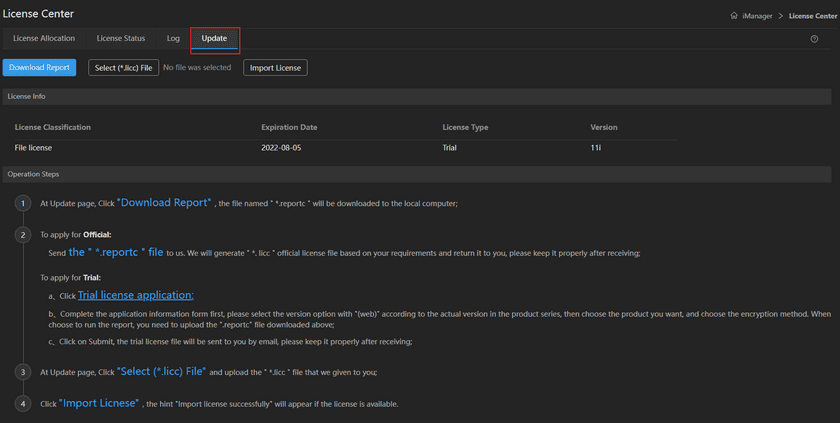
After the installation is complete, you need to import the license before you can use it. Here we take the import of the trial license as an example.
First, go to the SuperMap official website to apply for a trial license or purchase a formal license.
Visit the GIS Cloud Suite page. If there is no license, it will automatically jump to the License Center (Web version) page. Click Activate Update and import the license according to the operation process.
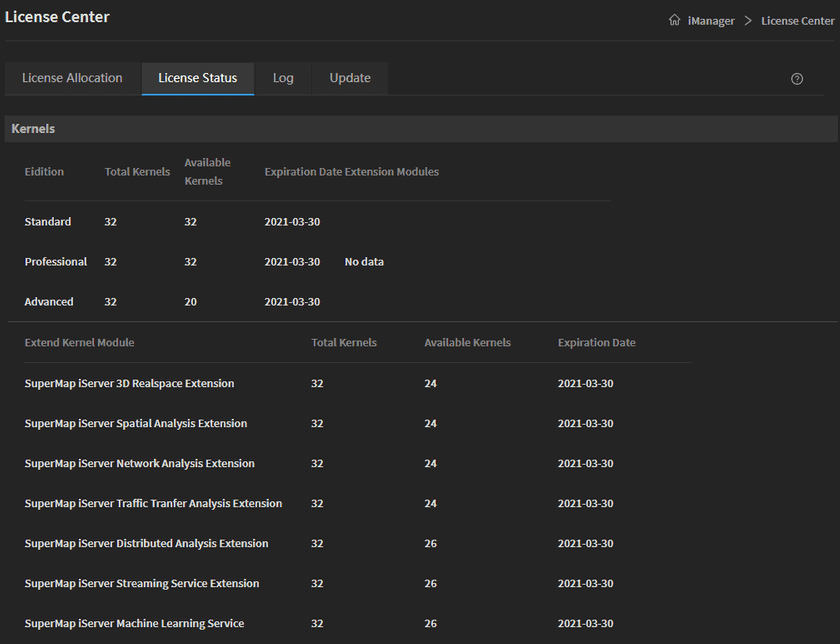
After the import is successful, you can see the license information under License Status.
Now you can use GIS Cloud Suite normally.