Tutorial
GIS Big Data
SuperMap iManager supports to ‘one-click’ creating GIS Big Data environment. As the GIS Big Data solution, the environment includes HBase, Spark, and HDFS, it supports a high effect storage, search, extend, process, and analysis for super large scaled spatial data.
For monitoring and managing, users can understand the associations between the services by topological diagram, check the account of the site, monitoring the service trace and service metrics, add services, allocate the resources for the site, search the services by keyworkds, and check the running pods in the site; users can also redeploy the services, adjust the specs of service, modify the images of service, expose/hide the services address, manual/automatic scaling the services, edit the YAML file of services, view the log of the services, and control the command pad of containers.
The main services in the GIS Cloud Suite environment are listed below:
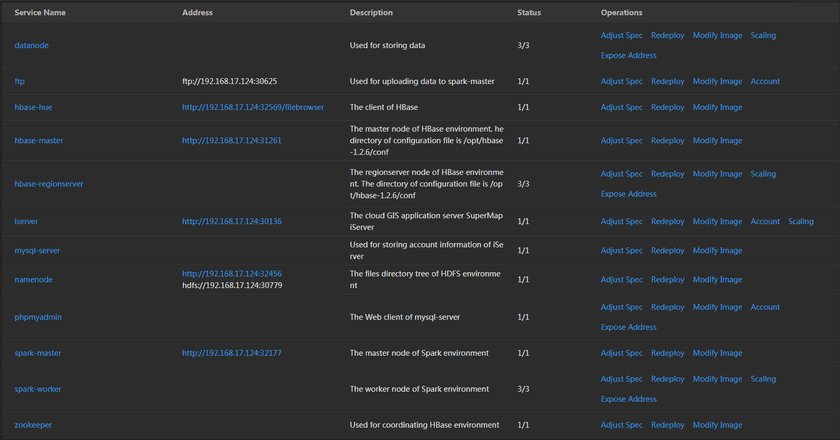
- DataNode: HDFS(distributed files system), to achieve unstructured data storage.
- FTP: The protocol of files transfer, used for transferring data between local storage and iServer.
- HBase-hue: The client of HBase database.
- HBase-master: The master node of HBase database.
- HBase-Regionserver: The regionserver node of HBase database.
- iServer: The cloud GIS application server SuperMap iServer, has the abilities of publishing 2D/3D services, managing, aggregation, and extention services.
- MySQL-Server: MySQL database, used for storing account information of iServer.
- Namenode: HDFS(distributed files system), files directory tree.
- PhpMyAdmin: The management tool of MySQL database, manage MySQL by Web client.
- Spark-Master: The master node of Spark computing engine.
- Spark-Worker: The worker node of Spark computing engine.
- Zookeeper: The distributed application coordinate service, it is an important component of HBase, used for coordinating HBase.